Table of Contents
ToggleThe full form of the GMAT is Graduate Management Admission Test. It is a multiple-choice, computer-adaptive, and standardized exam which is test 3 hours 7 minutes long and integral for MBA applications. There are four sections of the exam – verbal, quantitative, integrated reasoning, and analytical writing. The exam is developed by GMAC (Graduate Management Admission Council), which scores the test-takers between 200 and 800. The GMAT score holds the highest weightage in your MBA application at around 16%. However, many other factors are taken into consideration by the admission committees such as academic record, extracurricular activities, and professional experience among others.
In this article, we delve into all the aspects of the GMAT exam that you need to know – scoring, cost, registration, eligibility, importance, and other important aspects. Read on for more:
Eligibility Criteria for GMAT 2022
The factors that make you eligible for the GMAT exam are:
- Age: The test-taker must be a minimum of 18 years of age to be eligible for taking the exam
- Educational qualification: The candidate must have a bachelor’s degree from a recognized university or institute.
- Attempts: The applicants cannot apply more than five times for the exam in a year and more than once in a month.
How to Register For The GMAT?
You should register for the GMAT between 2 and 3 months before your tentative exam date to get ample choice for a slot. Keep the following information handy to complete your registration quickly: email id, phone number, address for correspondence, date of birth, nationality, educational qualifications, and payment information. Given below are the steps for registering for the GMAT exam
- Sign up on mba.com and enter the information required.
- Click on the Exam tab located at the top of the page and create a profile by filling in your country, address, phone number, and other information.
- Enter the optional information or skip it if you do not want to fill it.
- The GMAC processing team will verify your profile.
- Once verified, select up to three centers, suitable dates, and time slots to schedule your GMAT exam
- Lastly, pay the USD 250 registration fee to complete the process.
What Are The Different Sections of GMAT?
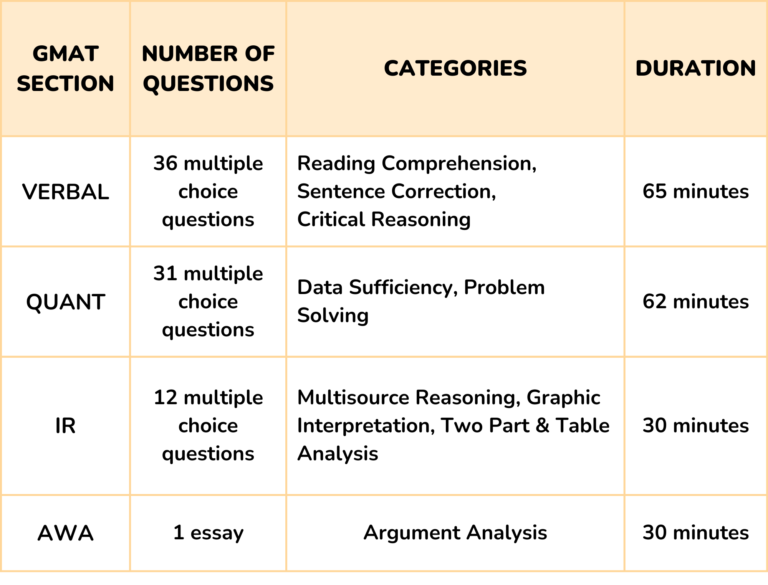
The GMAT exam has four sections – verbal, quant, analytical writing assessment, and integrated reasoning
Verbal Section
This section ascertains your command of the English language and ability to read critically. It consists of questions on critical reasoning, sentence correction, and reading comprehension, with each part testing a unique approach to your logic and reasoning.
Quantitative Section
The quant section consists of 31 multiple choice questions to be completed in 62 minutes, with questions on data sufficiency and problem-solving. This part of the exam is geared toward testing analytical understanding and application of basic mathematical concepts including algebra, arithmetic, and geometry.
Integrated Reasoning or IR section
This section consists of four types of questions: two-part analysis, table analysis, graphic interpretation, and multi-source reasoning. The section aims to understand a student’s ability to assess the information presented in graphs, tables, passages, or a combination of the three.
Analytical Writing Assessment or AWA Section
The essay under this section enables business schools to examine your writing skills, and the ability to analyze an argument and coherently communicate your opinions. You will not be required to offer your perspective on a topic, but rather to critically evaluate the author’s argument based on evidence and reasoning. The essays that you write within 30 minutes are scored by a human grader and a computer grading system, with the final mark consisting of the average of two scores. The section is scored separately, and not included in your total score out of 800.
To know more about the section, read Why Does the GMAT AWA Section Matter and AWA Template for Getting The Perfect 6
Why is GMAT Important?
While GMAT may seem merely a requirement for MBA, it is much more than that. GMAT is important for –
- Developing quantitative skills: Mastering integrated and quantitative reasoning sections of GMAT enables you to analyze massive data quickly, read patterns, and make decisions in a data-driven world.
- Enhancing reasoning and deduction: The four sections of the exam gauge your reasoning and deduction skills in different ways, thereby precipitating rational thinking and the ability to rapidly comprehend problems and formulate solutions.
- Admission to a premium b-school: Great GMAT scores are indispensable for enrolling in a reputed university, which in turn guarantees higher remuneration, better growth opportunities, and a strong network.
- Securing scholarships: As an international student, scholarships are essential for financing your studies but with increasing competition, it has become important to score 750+ to maximize your chances of winning a scholarship.
- Future employers: employers value your GMAT score and view them as an indicator of your quantitative skills, ability to analyze massive data quickly, and general academic distinction.
- Life skills: Diligent training for GMAT inculcates valuable life skills such as time management, discipline, focus, and perseverance. Further, it sharpens your communication skills which are integral for collaborating with different stakeholders.
How is GMAT Scored?
GMAT is a computer-adaptive test which means that the software continuously adapts itself to the student’s performance as they progress through the exam. If you choose the correct answer, the difficulty level increases. The final score is calculated based on the difficulty level of questions solved correctly and not merely the total number of correct answers. However, only the verbal and quant sections are computer-adaptive, not the remaining two.
A composite GMAT score is calculated based on your quant and verbal sub-scores. The exact details of this calculation are not publicly available. However, the important thing to note is that the calculation of the total GMAT score isn’t perfectly linear. Generally speaking, you’ll receive a better score if your quant and verbal marks are similar, and a somewhat lower score if you’re much better at one section than the other.
Read about GMAT scoring in detail: How is GMAT Score Calculated?
| GMAT Total Score | GMAT Percentile Ranking |
|---|---|
| 760-800 | 99% |
| 750 | 98% |
| 740 | 97% |
| 730 | 96% |
| 720 | 94% |
| 710 | 91% |
| 700 | 88% |
| 690 | 85% |
| 680 | 82% |
| 670 | 80% |
| 660 | 77% |
| 650 | 73% |
| 640 | 67% |
| 630 | 65% |
| 620 | 62% |
| 610 | 58% |
| 600 | 54% |
How Hard is The GMAT?
Of the 200,000 candidates who appear for the exam, a meager 6% succeed in scoring above 720. With the increasing competition and emphasis on GMAT scores by business schools, it has become imperative to perform well in the exam. But how hard is it to score well?
GMAT is a challenging exam due to many reasons. With its computer-adaptive format, the difficulty levels of the question keep varying and the candidate cannot skip a difficult question to come back to it later. The strict time deadline prevents the person from pondering over a complex question. The format and content also add to the difficulty of the exam.
However, it is important to note that GMAT is not a test of intelligence but reasoning and logic. It is about approach, strategies, and skills. With a bit of handholding and mentorship, you too can score a 740+ and get into your dream b-school. But that is only possible when you partner with the right trainer.
Train for GMAT with the only expert who has helped students achieve the PERFECT 800
When to Take the GMAT?
To decide the appropriate time for taking the exam, follow the following steps:
- Decide your target schools and note the dates of their multiple rounds of applications
- Determine the round in which you want to apply and keep at least 8-10 months for preparation of GMAT and writing applications.
- Try and write the GMAT before 6 months of the application deadline so that you also have the scope of retaking the exam if you are not satisfied with your first attempt.
- Spare sufficient time for writing your application essays and scholarship applications.
When Should You Retake The GMAT?
What should a candidate do if they have scored low on the exam? Should they retake it or not? How should they assess their options and next steps?
If you do not have the time to give another attempt, remember that in addition to GMAT scores, the admissions committee also harps upon your academic record, letters of recommendation, extracurricular activities, professional experience, essays, and more. Focus on these elements to make sure you can demonstrate spikes in your academic and professional lives and highlight your multifaceted personality.
However, based on your target school and scholarship goals, if your score is low you need to determine whether or not to retake. If you are a candidate from a competitive pool and your score is below the GMAT average score of last year’s class, consider giving another attempt because GMAT is the first filter applied to applicants. Do not be discouraged by your first attempt’s score.
At Enzo, we have seen a hike of 200-300 points in the students trained by our expert GMAT faculty. Still unsure? Sign up for your demo and have all your queries answered!














